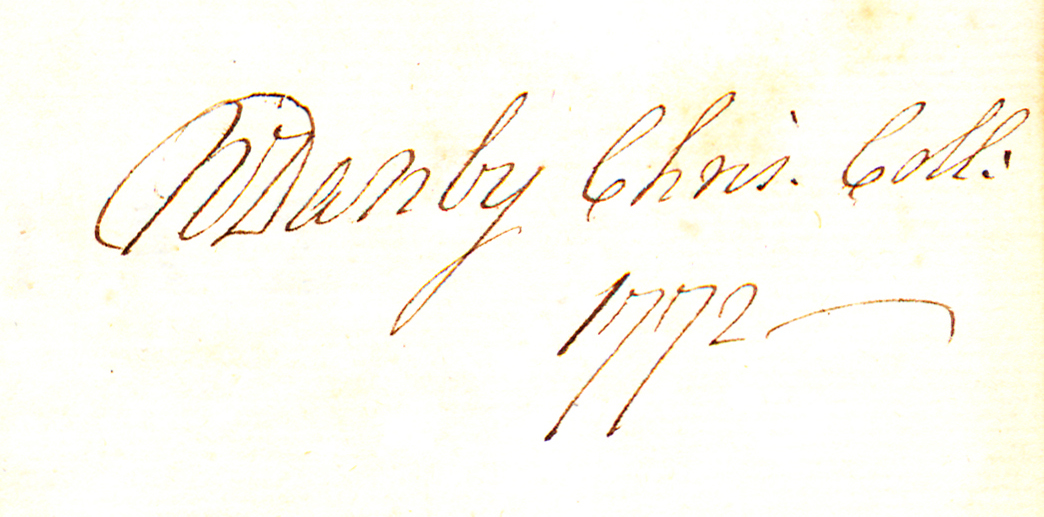Difference between revisions of "Homerou Odysseias"
m (Lktesar moved page Homērou Odysseias to Homerou Odysseias without leaving a redirect) |
m |
||
| (13 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{DISPLAYTITLE: | + | {{DISPLAYTITLE:''Της του Όμήρου Ίλιάδος ό τόμος πρότρος Δεγτερος''}} |
| − | |||
===by Homer=== | ===by Homer=== | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
{{BookPageInfoBox | {{BookPageInfoBox | ||
|imagename=Tēs tou Homērou Odysseias.jpg | |imagename=Tēs tou Homērou Odysseias.jpg | ||
| − | |link=https:// | + | |link=https://wm.primo.exlibrisgroup.com/permalink/01COWM_INST/g9pr7p/alma991021830259703196 |
|shorttitle=Tēs tou Homērou Odysseias | |shorttitle=Tēs tou Homērou Odysseias | ||
| − | |author=Homer | + | |author=[[:Category:Homer|Homer]] |
| − | |editor=James Moor and George Muirhead | + | |editor=[[:Category:James Moor|James Moor]] and [[:Category:George Muirhead|George Muirhead]] |
| − | |publoc=Glasguae: | + | |publoc=[[:Category:Glasgow|Glasguae: ]] |
|publisher=In aedibus Academicis, Excudebant R. et A. Foulis | |publisher=In aedibus Academicis, Excudebant R. et A. Foulis | ||
|year=1758 | |year=1758 | ||
| − | |lang=Greek | + | |lang=[[:Category:Greek|Greek]] |
|set=2 volumes in 1 | |set=2 volumes in 1 | ||
| − | |desc=Folio (34 cm.) | + | |desc=[[:Category:Folios|Folio]] (34 cm.) |
| + | |shelf=N-5 | ||
}}{{BookPageBookplate | }}{{BookPageBookplate | ||
|imagename=DanbyBookplatefromHomer.jpg | |imagename=DanbyBookplatefromHomer.jpg | ||
|display=left | |display=left | ||
|caption=Bookplate of William Danby, front pastedown. | |caption=Bookplate of William Danby, front pastedown. | ||
| − | }}Little is known about the life of Homer, the poet responsible for the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey''. Herodotus claimed Homer lived around 850 BCE, while modern scholars usually date his poems to the second half of the eighth century BCE.<ref>[http://www.oxfordreference.com/view/10.1093/acref/9780199548545.001.0001/acref-9780199548545-e-1550 "Homer”] in ''The Oxford Companion to Classical Literature'', ed. by M.C. Howatson (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2011).</ref> The Trojan War is estimated to have occurred at the end of the Mycenaean Age in Greece, around 1200 BCE, meaning that Homer was looking back four centuries to a heroic world much greater in his esteem, than the contemporary world. Homer relied on oral history to compose his poems; this provides some of the basis for the "separatist" view that the two epic poems were not written by the same person, but possibly by a combination of poets. The mixed dialect of Ionian Greek in which each poem was originally written indicates that both poems were written in the east Aegean. This is supported by contextual clues in the poems themselves. The two most plausible locations for the birth of Homer are Smyrna and Chios, but ancient Greeks viewed the poet as a blind minstrel wandering while he composed the poems, which were sung or chanted, accompanied by a lyre. | + | }}Little is known about the life of Homer, the poet responsible for the ''[[Homerou Iliados|Iliad]]'' and the ''Odyssey''. Herodotus claimed Homer lived around 850 BCE, while modern scholars usually date his poems to the second half of the eighth century BCE.<ref>[http://www.oxfordreference.com/view/10.1093/acref/9780199548545.001.0001/acref-9780199548545-e-1550 "Homer”] in ''The Oxford Companion to Classical Literature'', ed. by M.C. Howatson (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2011).</ref> The Trojan War is estimated to have occurred at the end of the Mycenaean Age in Greece, around 1200 BCE, meaning that Homer was looking back four centuries to a heroic world much greater in his esteem, than the contemporary world. Homer relied on oral history to compose his poems; this provides some of the basis for the "separatist" view that the two epic poems were not written by the same person, but possibly by a combination of poets. The mixed dialect of Ionian Greek in which each poem was originally written indicates that both poems were written in the east Aegean. This is supported by contextual clues in the poems themselves. The two most plausible locations for the birth of Homer are Smyrna and Chios, but ancient Greeks viewed the poet as a blind minstrel wandering while he composed the poems, which were sung or chanted, accompanied by a lyre. |
| − | + | ||
Homer’s ''Odyssey'' is an epic poem consisting of 24 books telling the story of the Trojan War hero Odysseus' ten-year journey trying to get home to his wife Penelope and son Telemachus in Ithaca, where Odysseus is king. This epic is distinct from the ''Iliad'' in that it is a more romantic than heroic/tragic poem. It is clear in the ''Odyssey'' who the “good” and “bad” characters are, and therefore with whom the readers (or more accurately the listeners, as it was intended to be recited orally) should emphathize. Odysseus is shown through much of Greek mythological writing as intelligent and crafty. He tricked Achilles into agreeing to join the Greeks against the Trojans, and tricked the Trojans with the giant wooden horse that helped to end the war. In the ''Odyssey'', Odysseus' familial devotion and "eternal human quality[y] of resolution" contrast with the barbaric creatures he meets on his adventures, as well as with the suitors attempting to woo his wife.<ref>"Homer" in ''Oxford Dictionary of the Classical World''.</ref> Odysseus' humaneness served as a model to Greek men, just as Penelope’s devotion to her husband and home showed Greek women how to behave. The strong moral themes in the ''Odyssey'' in no way take away from the exciting adventures Odysseus encountered, from the Cyclopes to the Lotus Eaters to the Sirens, and to tricking and defeating Penelope’s suitors.<br/> | Homer’s ''Odyssey'' is an epic poem consisting of 24 books telling the story of the Trojan War hero Odysseus' ten-year journey trying to get home to his wife Penelope and son Telemachus in Ithaca, where Odysseus is king. This epic is distinct from the ''Iliad'' in that it is a more romantic than heroic/tragic poem. It is clear in the ''Odyssey'' who the “good” and “bad” characters are, and therefore with whom the readers (or more accurately the listeners, as it was intended to be recited orally) should emphathize. Odysseus is shown through much of Greek mythological writing as intelligent and crafty. He tricked Achilles into agreeing to join the Greeks against the Trojans, and tricked the Trojans with the giant wooden horse that helped to end the war. In the ''Odyssey'', Odysseus' familial devotion and "eternal human quality[y] of resolution" contrast with the barbaric creatures he meets on his adventures, as well as with the suitors attempting to woo his wife.<ref>"Homer" in ''Oxford Dictionary of the Classical World''.</ref> Odysseus' humaneness served as a model to Greek men, just as Penelope’s devotion to her husband and home showed Greek women how to behave. The strong moral themes in the ''Odyssey'' in no way take away from the exciting adventures Odysseus encountered, from the Cyclopes to the Lotus Eaters to the Sirens, and to tricking and defeating Penelope’s suitors.<br/> | ||
{{BookPageBookplate | {{BookPageBookplate | ||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
|display=left | |display=left | ||
|caption=Bookplate of Roger Senhouse, front pastedown. | |caption=Bookplate of Roger Senhouse, front pastedown. | ||
| − | }}Bound in contemporary full diced brown calf with wide gilt tooled borders and five gilt stamped raised bands. Spines feature gilt lettered and elaborately gilt decorated and ornamented compartments. The edges are gilt-rolled. Includes the bookplates of William Danby, Lytton Strachey, and Roger Senhouse on the front pastedown. Signature "W Danby, Chris. Coll. 1772" on front flyleaf. Part of a combined set with [[ | + | }}Bound in contemporary full diced brown calf with wide gilt tooled borders and five gilt stamped raised bands. Spines feature gilt lettered and elaborately gilt decorated and ornamented compartments. The edges are gilt-rolled. Includes the bookplates of [[wikipedia:William Danby|William Danby (writer)]], [[wikipedia:Lytton Strachey|Lytton Strachey]], and [[wikipedia:Roger Senhouse|Roger Senhouse]] on the front pastedown. Signature "W Danby, Chris. Coll. 1772" on front flyleaf. Part of a combined set with [[Homerou Iliados|Tēs tou Homērou Iliados]]. Purchased from David Brass. |
| + | |||
| + | Images of the library's copy of this book are [https://flic.kr/s/aHsjMM2Xih available on Flickr]. View the record for this book in [https://wm.primo.exlibrisgroup.com/permalink/01COWM_INST/g9pr7p/alma991021830259703196 William & Mary's online catalog.] | ||
[[File:DanbySignaturefromHomer.jpg|right|thumb|200px|<center>Inscription, front flyleaf.</center>]] | [[File:DanbySignaturefromHomer.jpg|right|thumb|200px|<center>Inscription, front flyleaf.</center>]] | ||
| + | ==See also== | ||
| + | <div style="overflow: hidden;"> | ||
| + | *''[[Homerou Iliados]]'' | ||
| + | *''[[Homeri Ilias]]'' | ||
| + | *''[[Homerou Ilias kai Odysseia]]'' | ||
| + | *''[[Homerou Iliados|Tēs tou Homērou Iliados]]'' | ||
| + | *''[[Homērou Odysseia]]'' | ||
| + | *''[[Iliad of Homer|The Iliad of Homer]]'' | ||
| + | *''[[Ilias kai eis Auten Scholia ton Palaion|Ilias kai eis Auten Scholia ton Palaion = Homeri Ilias et Veterum in eam Scholia, quae Vulgo Appellantur Didymi]]'' | ||
| + | *[[Jefferson Inventory]] | ||
| + | *''[[Odyssey of Homer|The Odyssey of Homer]]'' | ||
| + | *''[[Incerti Scriptoris Graeci Fabulae Aliquot Homericae de Ulixis Erroribus|Incerti Scriptoris Graeci Fabulae Aliquot Homericae de Ulixis Erroribus, Ethice Explicatae]]'' | ||
| + | *[[George Wythe Room]] | ||
| + | *[[Wythe's Library]] | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| + | [[Category:George Muirhead]] | ||
[[Category:George Wythe Collection at William & Mary's Wolf Law Library]] | [[Category:George Wythe Collection at William & Mary's Wolf Law Library]] | ||
[[Category:Greek Literature]] | [[Category:Greek Literature]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Homer]] | ||
| + | [[Category:James Moor]] | ||
| + | [[Category:John Wayles Eppes' Books]] | ||
[[Category:Titles in Wythe's Library]] | [[Category:Titles in Wythe's Library]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Folios]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Glasgow]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Greek]] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:43, 7 September 2023
by Homer
| Tēs tou Homērou Odysseias | |
|
Title page from Tēs tou Homērou Odysseias, George Wythe Collection, Wolf Law Library, College of William & Mary. | |
| Author | Homer |
| Editor | James Moor and George Muirhead |
| Published | Glasguae: : In aedibus Academicis, Excudebant R. et A. Foulis |
| Date | 1758 |
| Language | Greek |
| Volumes | 2 volumes in 1 volume set |
| Desc. | Folio (34 cm.) |
| Location | Shelf N-5 |
Little is known about the life of Homer, the poet responsible for the Iliad and the Odyssey. Herodotus claimed Homer lived around 850 BCE, while modern scholars usually date his poems to the second half of the eighth century BCE.[1] The Trojan War is estimated to have occurred at the end of the Mycenaean Age in Greece, around 1200 BCE, meaning that Homer was looking back four centuries to a heroic world much greater in his esteem, than the contemporary world. Homer relied on oral history to compose his poems; this provides some of the basis for the "separatist" view that the two epic poems were not written by the same person, but possibly by a combination of poets. The mixed dialect of Ionian Greek in which each poem was originally written indicates that both poems were written in the east Aegean. This is supported by contextual clues in the poems themselves. The two most plausible locations for the birth of Homer are Smyrna and Chios, but ancient Greeks viewed the poet as a blind minstrel wandering while he composed the poems, which were sung or chanted, accompanied by a lyre.
Homer’s Odyssey is an epic poem consisting of 24 books telling the story of the Trojan War hero Odysseus' ten-year journey trying to get home to his wife Penelope and son Telemachus in Ithaca, where Odysseus is king. This epic is distinct from the Iliad in that it is a more romantic than heroic/tragic poem. It is clear in the Odyssey who the “good” and “bad” characters are, and therefore with whom the readers (or more accurately the listeners, as it was intended to be recited orally) should emphathize. Odysseus is shown through much of Greek mythological writing as intelligent and crafty. He tricked Achilles into agreeing to join the Greeks against the Trojans, and tricked the Trojans with the giant wooden horse that helped to end the war. In the Odyssey, Odysseus' familial devotion and "eternal human quality[y] of resolution" contrast with the barbaric creatures he meets on his adventures, as well as with the suitors attempting to woo his wife.[2] Odysseus' humaneness served as a model to Greek men, just as Penelope’s devotion to her husband and home showed Greek women how to behave. The strong moral themes in the Odyssey in no way take away from the exciting adventures Odysseus encountered, from the Cyclopes to the Lotus Eaters to the Sirens, and to tricking and defeating Penelope’s suitors.
Evidence for Inclusion in Wythe's Library
Listed in the Jefferson Inventory of Wythe's Library as "[Homeri] Odysseus. Gr. 2.v. fol. Foulis" and given by Thomas Jefferson to Dabney Carr. Both the Brown Bibliography[3] and George Wythe's Library[4] on LibraryThing list the 1758 Greek version of the Odyssey published by the Foulis Press. The Wolf Law Library purchased the same edition.
Description of the Wolf Law Library's copy
Bound in contemporary full diced brown calf with wide gilt tooled borders and five gilt stamped raised bands. Spines feature gilt lettered and elaborately gilt decorated and ornamented compartments. The edges are gilt-rolled. Includes the bookplates of William Danby (writer), Lytton Strachey, and Roger Senhouse on the front pastedown. Signature "W Danby, Chris. Coll. 1772" on front flyleaf. Part of a combined set with Tēs tou Homērou Iliados. Purchased from David Brass.
Images of the library's copy of this book are available on Flickr. View the record for this book in William & Mary's online catalog.
See also
References
- ↑ "Homer” in The Oxford Companion to Classical Literature, ed. by M.C. Howatson (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2011).
- ↑ "Homer" in Oxford Dictionary of the Classical World.
- ↑ Bennie Brown, "The Library of George Wythe of Williamsburg and Richmond," (unpublished manuscript, May, 2012) Microsoft Word file. Earlier edition available at: https://digitalarchive.wm.edu/handle/10288/13433
- ↑ LibraryThing, s. v. "Member: George Wythe," accessed on June 27, 2013, http://www.librarything.com/profile/GeorgeWythe