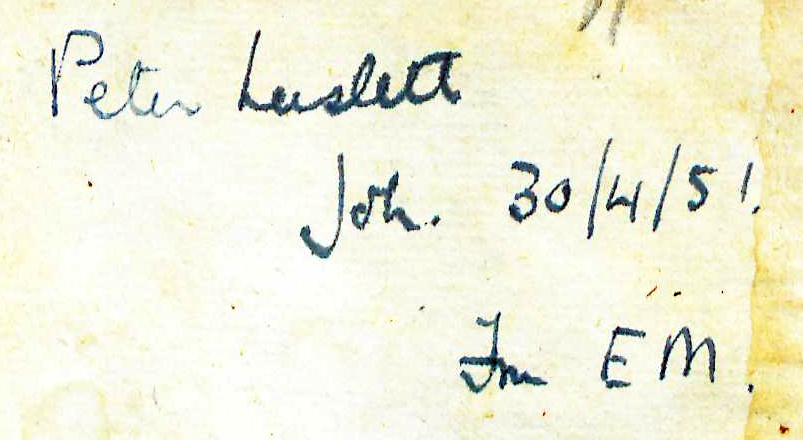Patriarcha, or, The Natural Power of Kings
by Sir Robert Filmer
| Patriarcha, or, The Natural Power of Kings | |
|
Title page from Patriarcha, or, The Natural Power of Kings, George Wythe Collection, Wolf Law Library, College of William & Mary. | |
| Author | Sir Robert Filmer |
| Published | London: Printed, and are to be sold by Walter Davis Book-binder |
| Date | 1680 |
| Edition | First |
| Language | English |
| Pages | 7, 141 |
| Desc. | 8vo (19 cm.) |

Patriarcha, Filmer’s best-known work, was written in about 1630 and remained unpublished for nearly 50 years.[3] Much dispute has arisen over Patriarcha’s original date of composition, but there is strong evidence to suggest that the manuscript was composed before 1631.[4] Patriarcha represents an attack on Calvinists and Jesuits, two enemies of royal power in Filmer’s view.[5] In it, Filmer espouses the doctrines of extreme believers of the Divine Right party: the family represents the appropriate model of all government, and subjects have a duty of passive obedience.[6] Filmer’s argument in Patriarcha traces the divine nature of the rule of patriarchs from the Old Testament onward, asserting that modern kings draw their power from the authority given by God to Adam, to Noah, and to Noah’s three sons (Shem, Ham, and Japheth) who ruled the three continents of the Biblical Old World.
After his death, Filmer’s writings gained notoriety as a target for criticism in John Locke’s first Treatise and became an object of ridicule for Locke’s Whig contemporaries, including James Tyrell and Algernon Sidney.[7]
Evidence for Inclusion in Wythe's Library
Dean's Memo[8] includes the 1760 edition of Political Discourses...viz. Patriarchs, or the Natural Power of Kings based on a reference in William Clarkin's biography of Wythe. In discussing Thomas Jefferson's education under Wythe, Clarkin states "[w]e do know that Jefferson studied ... Filmer's Patriarcha" but Clarkin provides no source of corroborating evidence.[9] Brown's Bibliography[10] lists a choice of two of Filmer's works, Observations Concerning the Original and Various Forms of Government (1696) or Patriarcha: or the Natural Power of Kings (1680). Brown does note Clarkin's reference and the lack of supporting evidence. The Wolf Law Library purchased the 1680 edition of Patriarcha: or the Natural Power of Kings.
Description of the Wolf Law Library's copy
Bound in period-style full blind calf. Includes a printed label "Petter Laslett Trinity College Cambridge" with the inscription "Gift of Edward Miller, 20 April, 1941. Bound by Gray, 1971" on the front pastedown. Also has the inscription "Peter Laslett, Joh. 30/4/51. Fm EM" on the front flyleaf. Purchased from Tavistock Books. View this book in William & Mary's online catalog.
References
- ↑ Glenn Burgess, [http://www.oxforddnb.com.proxy.wm.edu/view/article/9424 "Filmer, Sir Robert (1588?–1653)" in Oxford Dictionary of National Biography (Oxford University Press, 2004- ), accessed 3 Oct 2013.
- ↑ The Bar Council website, s.v. "Being Called to the Bar," accessed October 3, 2013 http://www.barcouncil.org.uk/becoming-a-barrister/how-to-become-a-barrister/being-called-to-the-bar.
- ↑ Glenn Burgess, "Filmer, Sir Robert."
- ↑ Ibid, "There is good internal evidence to suggest that the manuscript of the work now in the University of Chicago Library Codex MS 413 was composed before 1631."
- ↑ The Oxford Companion to Philosophy, ed. R.S. Downie and Ted Honderich (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1995), 280.
- ↑ Ibid.
- ↑ Glenn Burgess, "Filmer, Sir Robert."
- ↑ Memorandum from Barbara C. Dean, Colonial Williamsburg Found., to Mrs. Stiverson, Colonial Williamsburg Found. (June 16, 1975), 11 (on file at Wolf Law Library, College of William & Mary).
- ↑ William Clarkin, Serene Patriot: A Life of George Wythe (Albany, New York: Alan Publications, 1970), 42.
- ↑ Bennie Brown, "The Library of George Wythe of Williamsburg and Richmond," (unpublished manuscript, May, 2012) Microsoft Word file. Earlier edition available at: https://digitalarchive.wm.edu/handle/10288/13433