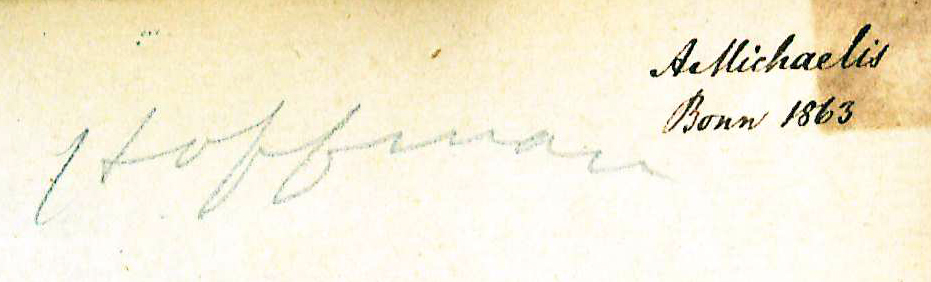Difference between revisions of "Opera Omnia, Graece et Latine"
m |
|||
| (15 intermediate revisions by 9 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{DISPLAYTITLE:''Opera Omnia, Graece et Latine''}} | {{DISPLAYTITLE:''Opera Omnia, Graece et Latine''}} | ||
===by Lysias=== | ===by Lysias=== | ||
| − | |||
{{BookPageInfoBox | {{BookPageInfoBox | ||
|imagename=LysiasOperaOmnia1783.jpg | |imagename=LysiasOperaOmnia1783.jpg | ||
| − | |link=https:// | + | |link=https://wm.primo.exlibrisgroup.com/permalink/01COWM_INST/g9pr7p/alma991023618989703196 |
| − | |shorttitle= | + | |shorttitle=Works of Lysias |
| − | |author=Lysias | + | |author=[[:Category:Lysias|Lysias]] |
| − | |editor=Abbé Athanase Auger | + | |editor=[[:Category:Athanase Auger|Abbé Athanase Auger]] |
|edition=Seventh impression; Fifth revised | |edition=Seventh impression; Fifth revised | ||
| − | |lang=Latin | + | |lang=[[:Category:Latin|Latin]] |
| − | |publoc=Paris | + | |publoc=[[:Category:Paris|Paris]] |
|publisher=Franc. Ambr. Didot L'ainé | |publisher=Franc. Ambr. Didot L'ainé | ||
|year=1783 | |year=1783 | ||
|set=2 | |set=2 | ||
| − | |desc=8vo (20 cm) | + | |desc=[[:Category:Octavos|8vo]] (20 cm) |
| + | |shelf=I-3 | ||
}}{{BookPageBookplate | }}{{BookPageBookplate | ||
|imagename=LysiasOperaOmnia1783Bookplate.jpg | |imagename=LysiasOperaOmnia1783Bookplate.jpg | ||
|display=left | |display=left | ||
|caption=Bookplate, front pastedown. | |caption=Bookplate, front pastedown. | ||
| − | }}Lysias was an Attic (Greek) orator born between 458 and 473 BCE and who died c.380 BCE.<ref>[http://www.oxfordreference.com/view/10.1093/acref/9780199548545.001.0001/acref-9780199548545-e-1865 | + | }}[[wikipedia:Lysias|Lysias]] was an Attic (Greek) orator born between 458 and 473 BCE and who died c.380 BCE.<ref>M.C. Howatson, ed., "[http://www.oxfordreference.com/view/10.1093/acref/9780199548545.001.0001/acref-9780199548545-e-1865 Ly'sias]" in ''The Oxford Companion to Classical Literature'' (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2011).</ref> He was born to [[wikipedia:Cephalus#Historical persons|Cephalus]], a wealthy Syracusan who had known [[wikipedia:Pericles|Pericles]]. Pericles had convinced Cephalus to move to Athens as a ''metic'' (resident alien), so Lysias and his family grew up Greek with a very successful shield-making family business. The home of Lysias' eldest brother [[wikipedia:Polemarchus|Polemarchus]] is the setting for Plato's ''Republic'', where Polemarchus and Cephalus speak in the opening discussion.<ref>Ibid.</ref> |
| − | + | ||
| − | Lysias and Polemarchus went to the panhellenic colony of Thurii in south Italy after their | + | Lysias and Polemarchus went to the panhellenic colony of [[wikipedia:Thurii|Thurii]] in south Italy after their father's death, where Lysias studied rhetoric.<ref>John Roberts, ed., "[http://www.oxfordreference.com/view/10.1093/acref/9780192801463.001.0001/acref-9780192801463-e-1323 Lysias]" in ''Oxford Dictionary of the Classical World'' (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2007).</ref> They were expelled in 413 BCE as Athenian sympathizers, and returned to Athens.<ref>Howatson, "Ly'sias."</ref> The brothers were arrested in 403 by the [[wikipedia: Thirty Tyrants| Thirty Tyrants]] who alleged disaffection, but according to Lysias in his 12th speech, really wanted to confiscate their substantial property.<ref>Roberts, "Lysias."</ref> The Thirty Tyrants killed Polemarchus, but Lysias escaped and then supported the democratic counter-revolutionaries.<ref>Ibid.</ref> |
| − | + | ||
| − | Lysias was quite poor at this point, so he turned to professional speech-writing and became very successful. As a ''metic'', he could not appear in court | + | Lysias was quite poor at this point, so he turned to professional speech-writing and became very successful. As a ''metic'', he could not appear in court — therefore someone else had to deliver his speeches. However, he was able to deliver his first career speech "Against Eratosthenes" (speech 12) to a court of inquiry during the trial of the alleged murderer of his brother Polemarchus.<ref>Howatson, "Ly'sias."</ref> Also as a poet, Lysias composed over two-hundred poems. Only thirty-five survive, with only twenty-three complete. He was admired for the simplicity and precise, ordered nature of his language.<ref>Ibid.</ref> |
| − | + | ||
| − | This particular work is a first edition of | + | This particular work is a first edition of "All the Works of Lysias, Greek and Latin" in two volumes. In the first volume, after a prologue and a comment on the work of critics, there is a table of contents covering both the first and second volumes. All of the speeches have the original Greek and translated Latin on parallel pages. |
| − | [[File:LysiasOperaOmnia1783Inscription.jpg|left|thumb| | + | |
| + | [[File:LysiasOperaOmnia1783Inscription.jpg|left|thumb|450px|<center>Inscriptions, front free endpaper.</center>]] | ||
==Evidence for Inclusion in Wythe's Library== | ==Evidence for Inclusion in Wythe's Library== | ||
| − | Listed in the [[Jefferson Inventory]] of [[Wythe's Library]] as | + | Listed in the [[Jefferson Inventory]] of [[Wythe's Library]] as "Lysiae opera omnia. Gr. Lat. 2.v. 8vo." and given by [[Thomas Jefferson]] to his grandson [[Thomas Jefferson Randolph]]. Both the [https://digitalarchive.wm.edu/handle/10288/13433 Brown Bibliography]<ref>Bennie Brown, "The Library of George Wythe of Williamsburg and Richmond," (unpublished manuscript, May, 2012) Microsoft Word file.</ref> and [http://www.librarything.com/profile/GeorgeWythe George Wythe's Library]<ref>''LibraryThing'', s.v. "[http://www.librarything.com/profile/GeorgeWythe Member: George Wythe]," accessed on February 26, 2014.</ref> on LibraryThing list the 1783 Paris edition of ''Lysiae Opera Omnia'' as the title and edition for Jefferson's entry. The Wolf Law Library found a copy of volume one of the 1783 edition and purchased it. |
==Description of the Wolf Law Library's copy== | ==Description of the Wolf Law Library's copy== | ||
Set incomplete. Library lacks volume two. Volume one has marbled boards and full leather spine with 4 raised bands and gilt lettering. Includes the bookplate of "O.J." with the motto "Inter folia fructus" (fruit among the leaves) on the front pastedown. Signed "Hoffman" and "A. Michaelis, Bonn 1863" on the front free endpaper. | Set incomplete. Library lacks volume two. Volume one has marbled boards and full leather spine with 4 raised bands and gilt lettering. Includes the bookplate of "O.J." with the motto "Inter folia fructus" (fruit among the leaves) on the front pastedown. Signed "Hoffman" and "A. Michaelis, Bonn 1863" on the front free endpaper. | ||
| − | [https:// | + | Images of the library's copy of this book are [https://www.flickr.com/photos/wolflawlibrary/sets/72157637697003665 available on Flickr.] View the record for this book in [https://wm.primo.exlibrisgroup.com/permalink/01COWM_INST/g9pr7p/alma991023618989703196 William & Mary's online catalog] |
| − | + | ||
| + | ===Full text=== | ||
| + | <div style="overflow: hidden;"> | ||
| + | *[http://lawlibrary.wm.edu/wythepedia/library/LysiasOperaOmnia1783Vol1.pdf Volume I] (14MB PDF) | ||
| + | *Volume II | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==See also== | ||
| + | *[[George Wythe Room]] | ||
| + | *[[Jefferson Inventory]] | ||
| + | *[[Wythe's Library]] | ||
| + | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| + | __NOTOC__ | ||
| + | [[Category:Athanase Auger]] | ||
[[Category:George Wythe Collection at William & Mary's Wolf Law Library]] | [[Category:George Wythe Collection at William & Mary's Wolf Law Library]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Thomas Jefferson Randolph's Books]] | ||
[[Category:Language and Rhetoric]] | [[Category:Language and Rhetoric]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Lysias]] | ||
[[Category:Titles in Wythe's Library]] | [[Category:Titles in Wythe's Library]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Latin]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Octavos]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Paris]] | ||
Latest revision as of 09:07, 15 January 2025
by Lysias
| Works of Lysias | |
|
Title page from Works of Lysias, George Wythe Collection, Wolf Law Library, College of William & Mary. | |
| Author | Lysias |
| Editor | Abbé Athanase Auger |
| Published | Paris: Franc. Ambr. Didot L'ainé |
| Date | 1783 |
| Edition | Seventh impression; Fifth revised |
| Language | Latin |
| Volumes | 2 volume set |
| Desc. | 8vo (20 cm) |
| Location | Shelf I-3 |
Lysias was an Attic (Greek) orator born between 458 and 473 BCE and who died c.380 BCE.[1] He was born to Cephalus, a wealthy Syracusan who had known Pericles. Pericles had convinced Cephalus to move to Athens as a metic (resident alien), so Lysias and his family grew up Greek with a very successful shield-making family business. The home of Lysias' eldest brother Polemarchus is the setting for Plato's Republic, where Polemarchus and Cephalus speak in the opening discussion.[2]
Lysias and Polemarchus went to the panhellenic colony of Thurii in south Italy after their father's death, where Lysias studied rhetoric.[3] They were expelled in 413 BCE as Athenian sympathizers, and returned to Athens.[4] The brothers were arrested in 403 by the Thirty Tyrants who alleged disaffection, but according to Lysias in his 12th speech, really wanted to confiscate their substantial property.[5] The Thirty Tyrants killed Polemarchus, but Lysias escaped and then supported the democratic counter-revolutionaries.[6]
Lysias was quite poor at this point, so he turned to professional speech-writing and became very successful. As a metic, he could not appear in court — therefore someone else had to deliver his speeches. However, he was able to deliver his first career speech "Against Eratosthenes" (speech 12) to a court of inquiry during the trial of the alleged murderer of his brother Polemarchus.[7] Also as a poet, Lysias composed over two-hundred poems. Only thirty-five survive, with only twenty-three complete. He was admired for the simplicity and precise, ordered nature of his language.[8]
This particular work is a first edition of "All the Works of Lysias, Greek and Latin" in two volumes. In the first volume, after a prologue and a comment on the work of critics, there is a table of contents covering both the first and second volumes. All of the speeches have the original Greek and translated Latin on parallel pages.
Evidence for Inclusion in Wythe's Library
Listed in the Jefferson Inventory of Wythe's Library as "Lysiae opera omnia. Gr. Lat. 2.v. 8vo." and given by Thomas Jefferson to his grandson Thomas Jefferson Randolph. Both the Brown Bibliography[9] and George Wythe's Library[10] on LibraryThing list the 1783 Paris edition of Lysiae Opera Omnia as the title and edition for Jefferson's entry. The Wolf Law Library found a copy of volume one of the 1783 edition and purchased it.
Description of the Wolf Law Library's copy
Set incomplete. Library lacks volume two. Volume one has marbled boards and full leather spine with 4 raised bands and gilt lettering. Includes the bookplate of "O.J." with the motto "Inter folia fructus" (fruit among the leaves) on the front pastedown. Signed "Hoffman" and "A. Michaelis, Bonn 1863" on the front free endpaper.
Images of the library's copy of this book are available on Flickr. View the record for this book in William & Mary's online catalog
Full text
See also
References
- ↑ M.C. Howatson, ed., "Ly'sias" in The Oxford Companion to Classical Literature (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2011).
- ↑ Ibid.
- ↑ John Roberts, ed., "Lysias" in Oxford Dictionary of the Classical World (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2007).
- ↑ Howatson, "Ly'sias."
- ↑ Roberts, "Lysias."
- ↑ Ibid.
- ↑ Howatson, "Ly'sias."
- ↑ Ibid.
- ↑ Bennie Brown, "The Library of George Wythe of Williamsburg and Richmond," (unpublished manuscript, May, 2012) Microsoft Word file.
- ↑ LibraryThing, s.v. "Member: George Wythe," accessed on February 26, 2014.